ModelClient¶
ModelClient is the standardized protocol and base class for all model inference SDKs (either via APIs or local) to communicate with AdalFlow internal components.
Therefore, by switching out the ModelClient in a Generator, Embedder, or Retriever (those components that take models), you can make these functional components model-agnostic.
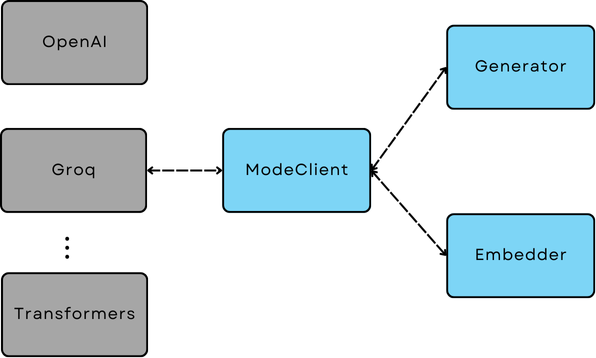
The bridge between all model inference SDKs and internal components in AdalFlow¶
Note
All users are encouraged to customize their own ModelClient whenever needed. You can refer to our code in components.model_client directory.
Model Inference SDKs¶
With cloud API providers like OpenAI, Groq, and Anthropic, it often comes with a sync and an async client via their SDKs. For example:
from openai import OpenAI, AsyncOpenAI
sync_client = OpenAI()
async_client = AsyncOpenAI()
# sync call using APIs
response = sync_client.chat.completions.create(...)
For local models, such as using huggingface transformers, you need to create these model inference SDKs yourself.
How you do this is highly flexible.
Here is an example of using a local embedding model (e.g., thenlper/gte-base) as a model (Refer to TransformerEmbedder for details).
It really is just normal model inference code.
Note
Integrating to different model providers such as DeepSeek, Mixtral etc has gotten easier as most providers are converging to just use OpenAI sdks and point to their own model endpoints.
ModelClient Protocol¶
A model client can be used to manage different types of models, we defined a ModelType to categorize the model type.
class ModelType(Enum):
EMBEDDER = auto()
LLM = auto()
RERANKER = auto()
UNDEFINED = auto()
We designed 6 abstract methods in the ModelClient class that can be implemented by subclasses to integrate with different model inference SDKs.
We will use OpenAIClient as the cloud API example and TransformersClient along with the local inference code TransformerEmbedder as an example for local model clients.
First, we offer two methods, init_async_client and init_sync_client, for subclasses to initialize the SDK client.
You can refer to OpenAIClient to see how these methods, along with the __init__ method, are implemented:
This is how TransformerClient does the same thing:
class TransformersClient(ModelClient):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.sync_client = self.init_sync_client()
self.async_client = None
support_model_list = {
"thenlper/gte-base": {
"type": ModelType.EMBEDDER,
}
}
def init_sync_client(self):
return TransformerEmbedder()
Second, we use convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs for subclasses to convert AdalFlow inputs into the api_kwargs (SDK arguments).
def convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
self,
input: Optional[Any] = None,
model_kwargs: Dict = {},
model_type: ModelType = ModelType.UNDEFINED,
) -> Dict:
raise NotImplementedError(
f"{type(self).__name__} must implement _combine_input_and_model_kwargs method"
)
This is how OpenAIClient implements this method:
def convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
self,
input: Optional[Any] = None,
model_kwargs: Dict = {},
model_type: ModelType = ModelType.UNDEFINED,
) -> Dict:
final_model_kwargs = model_kwargs.copy()
if model_type == ModelType.EMBEDDER:
if isinstance(input, str):
input = [input]
# convert input to input
assert isinstance(input, Sequence), "input must be a sequence of text"
final_model_kwargs["input"] = input
elif model_type == ModelType.LLM:
messages: List[Dict[str, str]] = []
if input is not None and input != "":
messages.append({"role": "system", "content": input})
assert isinstance(
messages, Sequence
), "input must be a sequence of messages"
final_model_kwargs["messages"] = messages
else:
raise ValueError(f"model_type {model_type} is not supported")
return final_model_kwargs
For embedding, as Embedder takes both str and List[str] as input, we need to convert the input to a list of strings that is acceptable by the SDK.
For LLM, as Generator will takes a prompt_kwargs`(dict) and convert it into a single string, thus we need to convert the input to a list of messages.
For Rerankers, you can refer to :class:`CohereAPIClient<components.model_client.cohere_client.CohereAPIClient> for an example.
This is how TransformerClient does the same thing:
def convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
self,
input: Any,
model_kwargs: dict = {},
model_type: ModelType = ModelType.UNDEFINED,
) -> dict:
final_model_kwargs = model_kwargs.copy()
if model_type == ModelType.EMBEDDER:
final_model_kwargs["input"] = input
return final_model_kwargs
else:
raise ValueError(f"model_type {model_type} is not supported")
In addition, you can add any method that parses the SDK-specific output to a format compatible with AdalFlow components.
Typically, an LLM needs to use parse_chat_completion to parse the completion to text and parse_embedding_response to parse the embedding response to a structure that AdalFlow components can understand.
You can refer to OpenAIClient for API embedding model integration and TransformersClient for local embedding model integration.
Lastly, the call and acall methods are used to call model inference via their own arguments. We encourage subclasses to provide error handling and retry mechanisms in these methods.
The OpenAIClient example:
def call(self, api_kwargs: Dict = {}, model_type: ModelType = ModelType.UNDEFINED):
if model_type == ModelType.EMBEDDER:
return self.sync_client.embeddings.create(**api_kwargs)
elif model_type == ModelType.LLM:
return self.sync_client.chat.completions.create(**api_kwargs)
else:
raise ValueError(f"model_type {model_type} is not supported")
The TransformerClient example:
def call(self, api_kwargs: Dict = {}, model_type: ModelType = ModelType.UNDEFINED):
return self.sync_client(**api_kwargs)
O ur library currently integrates with six providers: OpenAI, Groq, Anthropic, Huggingface, Google, and Cohere. Please check out ModelClient Integration.
Use ModelClient directly¶
Though ModelClient is often managed in a Generator, Embedder, or Retriever component, you can use it directly if you plan to write your own component.
Here is an example of using OpenAIClient directly, first on an LLM model:
from adalflow.components.model_client import OpenAIClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
from adalflow.utils import setup_env
setup_env()
openai_client = OpenAIClient()
query = "What is the capital of France?"
# try LLM model
model_type = ModelType.LLM
prompt = f"User: {query}\n"
model_kwargs = {"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo", "temperature": 0.5, "max_tokens": 100}
api_kwargs = openai_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(input=prompt,
model_kwargs=model_kwargs,
model_type=model_type)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}")
response = openai_client.call(api_kwargs=api_kwargs, model_type=model_type)
response_text = openai_client.parse_chat_completion(response)
print(f"response_text: {response_text}")
The output will be:
api_kwargs: {'model': 'gpt-3.5-turbo', 'temperature': 0.5, 'max_tokens': 100, 'messages': [{'role': 'system', 'content': 'User: What is the capital of France?\n'}]}
response_text: The capital of France is Paris.
Then on Embedder model:
# try embedding model
model_type = ModelType.EMBEDDER
# do batch embedding
input = [query] * 2
model_kwargs = {"model": "text-embedding-3-small", "dimensions": 8, "encoding_format": "float"}
api_kwargs = openai_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(input=input, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, model_type=model_type)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}")
response = openai_client.call(api_kwargs=api_kwargs, model_type=model_type)
reponse_embedder_output = openai_client.parse_embedding_response(response)
print(f"reponse_embedder_output: {reponse_embedder_output}")
The output will be:
api_kwargs: {'model': 'text-embedding-3-small', 'dimensions': 8, 'encoding_format': 'float', 'input': ['What is the capital of France?', 'What is the capital of France?']}
reponse_embedder_output: EmbedderOutput(data=[Embedding(embedding=[0.6175549, 0.24047995, 0.4509756, 0.37041178, -0.33437008, -0.050995983, -0.24366009, 0.21549304], index=0), Embedding(embedding=[0.6175549, 0.24047995, 0.4509756, 0.37041178, -0.33437008, -0.050995983, -0.24366009, 0.21549304], index=1)], model='text-embedding-3-small', usage=Usage(prompt_tokens=14, total_tokens=14), error=None, raw_response=None)
OPENAI EMBEDDER - Embedding Processing Example¶
In this example, we are using a collection of embeddings to demonstrate different functionalities such as calculating semantic similarity, finding nearest neighbors, and averaging embeddings. Below is the Python code used to achieve these tasks:
from typing import List
import numpy as np
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType, EmbedderOutput
from adalflow.components.model_client import OpenAIClient
from dataclasses import dataclass
from enum import Enum
from numpy.linalg import norm
Data Classes
We use two dataclass types to structure the collection and usage data:
EmbeddingCollection: Stores an individual embedding collection and its corresponding index. Usage: Keeps track of token usage, such as prompt_tokens and total_tokens.
@dataclass
class EmbeddingCollection:
collection: List[float]
cindex: int
@dataclass
class Usage:
prompt_tokens: int
total_tokens: int
The following function, get_openai_embedding, sends a request to the OpenAI API to retrieve embeddings for a given text. It sets the model type to EMBEDDER, prepares the required model-specific parameters, and processes the response:
openai_client = OpenAIClient()
def get_openai_embedding(text):
# Set model type to EMBEDDER for embedding functionality
model_type = ModelType.EMBEDDER
# Prepare input and model-specific parameters
input = text
model_kwargs = {
"model": "text-embedding-3-small",
"dimensions": 8,
"encoding_format": "float",
}
# Convert inputs to the required API format
api_kwargs = openai_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=input, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, model_type=model_type
)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}") # Debug output to verify API arguments
# Call OpenAI API and parse response for embeddings
response = openai_client.call(api_kwargs=api_kwargs, model_type=model_type)
reponse_embedder_output = openai_client.parse_embedding_response(response)
print(
f"reponse_embedder_output: {reponse_embedder_output}"
) # Debug output to verify embeddings
return reponse_embedder_output
Embedding Processing
The function process_embeddings takes in a collection of embeddings and provides utilities for calculating similarity, averaging embeddings, and finding nearest neighbors:
Similarity: Measures the cosine similarity between two embeddings. Average Embedding: Computes the mean embedding across a set of embeddings. Nearest Neighbors: Identifies the top-k nearest neighbors based on cosine similarity.
def process_embeddings(embeddings_collection):
# Extract embedding data for each item in the collection
embeddingOutput = [emb.collection for emb in embeddings_collection]
embeddingDataList = [each_emb_out.data for each_emb_out in embeddingOutput]
embeddingList = [
each_item.embedding
for each_emb_data in embeddingDataList
for each_item in each_emb_data
]
# Convert to numpy array for easier manipulation and calculations
embeddings_array = np.array(embeddingList)
def calculate_similarity(emb1, emb2):
# Compute cosine similarity between two embeddings
return np.dot(emb1, emb2) / (norm(emb1) * norm(emb2))
def get_average_embedding(embeddings_list):
# Calculate the mean embedding across a list of embeddings
return np.mean(embeddings_list, axis=0)
def find_nearest_neighbors(
query_index: int, embedding_list: List[List[float]], k: int = 5
):
# Find top-k most similar embeddings to a query embedding, based on cosine similarity
query_embedding = embedding_list[query_index]
similarities = [
(i, calculate_similarity(query_embedding, emb))
for i, emb in enumerate(embedding_list)
if i != query_index
]
return sorted(similarities, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[:k]
# Return dictionary of functions and processed data for further use
return {
"embeddings_array": embeddings_array,
"calculate_similarity": calculate_similarity,
"average_embedding": get_average_embedding,
"find_nearest_neighbors": find_nearest_neighbors,
}
The function demonstrate_embeddings_usage showcases how to analyze semantic similarities, find nearest neighbors, and calculate average embeddings for sample texts. It selects random texts, compares their similarities, finds nearest neighbors for a specific query, and compares average embeddings for texts containing “Paris”.
# Demonstrate embeddings usage with sample data
def demonstrate_embeddings_usage(sample_embeddings, input_text_list):
# Initialize processor and retrieve embeddings array
processor = process_embeddings(sample_embeddings)
embeddings = processor["embeddings_array"]
print("1. Analyzing Semantic Similarities:")
print("-" * 50)
# Select a few random indices for similarity testing
num_indices = 5
assert len(input_text_list) == len(embeddings)
indices = np.random.choice(len(input_text_list), num_indices, replace=False)
selected_text = np.array(input_text_list)[indices]
selected_embeddings = np.array(embeddings)[indices]
# Display selected texts and their embeddings
print("Selected indices:", indices)
print("Selected elements from array1:", selected_text)
print("Selected elements from array2:", selected_embeddings)
# Calculate similarity between each pair of selected texts
for i in range(len(selected_text)):
for j in range(i + 1, len(selected_text)):
similarity = processor["calculate_similarity"](
selected_embeddings[i], selected_embeddings[j]
)
print(f"\nComparing:\n'{selected_text[i]}' \nwith:\n'{selected_text[j]}'")
print(f"Similarity score: {similarity:.4f}")
print("\n2. Finding Nearest Neighbors:")
print("-" * 50)
# Find and display the 3 nearest neighbors for the first text
query_idx = 0
neighbors = processor["find_nearest_neighbors"](query_idx, embeddings, k=3)
print(f"\nQuery text: '{input_text_list[query_idx]}'")
print("\nNearest neighbors:")
for idx, similarity in neighbors:
print(f"- '{input_text_list[idx]}' (similarity: {similarity:.4f})")
print("\n3. Using Average Embeddings:")
print("-" * 50)
# Calculate and compare the average embedding for texts containing "Paris"
paris_indices = [i for i, text in enumerate(input_text_list) if "Paris" in text]
paris_embeddings = embeddings[paris_indices]
avg_paris_embedding = processor["average_embedding"](paris_embeddings)
print("\nComparing average 'Paris' embedding with all texts:")
for i, text in enumerate(input_text_list):
similarity = processor["calculate_similarity"](
avg_paris_embedding, embeddings[i]
)
print(f"- '{text}' (similarity: {similarity:.4f})")
Running the Model Client
Finally, we run the model client by initializing a set of sample texts, generating their embeddings, and using the embedding processing functions to analyze similarities and neighbors.
def run_model_client_embedding_usage():
# Define a set of sample texts to test embedding and similarity functionalities
sample_texts = [
"What is the capital of France?",
"Paris is the capital of France.",
"What is the population of France?",
"How big is Paris?",
"What is the weather like in Paris?",
]
# Duplicate each sample text to form an input list with repeated entries (for embedding testing)
input_text_list = [text for text in sample_texts for _ in range(2)]
# Generate embeddings for each text in the input list, and store them in an EmbeddingCollection
embeddings_collection = [
EmbeddingCollection(collection=get_openai_embedding(text), cindex=i)
for i, text in enumerate(input_text_list)
]
print(
embeddings_collection
) # Debugging output to verify embeddings collection content
# Demonstrate the usage of embeddings by analyzing similarities, finding neighbors, etc.
demonstrate_embeddings_usage(embeddings_collection, input_text_list)
To execute the complete example, simply call the run_model_client_embedding_usage() function:
run_model_client_embedding_usage()
This will trigger the embedding retrieval and processing functions, and you will see the results printed out, demonstrating how embeddings can be used for similarity analysis, neighbor finding, and averaging.
OPENAI LLM Chat - Multichat Usage¶
This example demonstrates how to create a multichat system using OpenAI’s LLM with adalflow, where the assistant’s responses depend on the entire conversation history. This allows for a more dynamic and context-aware conversation flow.
from adalflow.components.model_client import OpenAIClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
from adalflow.utils import setup_env
from typing import List, Dict
ChatConversation Class
Here, we define a ChatConversation class to manage the conversation history and make API calls to the OpenAI model. The assistant’s responses are generated based on the entire conversation history.
class ChatConversation:
def __init__(self):
# Initialize the OpenAI client for managing API calls
self.openai_client = OpenAIClient()
# Initialize an empty conversation history to store chat messages
self.conversation_history: str = ""
# Model parameters to customize the API call
self.model_kwargs = {
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"temperature": 0.5, # Controls randomness; 0.5 for balanced responses
"max_tokens": 100, # Limits the response length
}
def add_user_message(self, message: str):
"""Add a user message to the conversation history"""
self.conversation_history += (
f"<USER> {message} </USER>" # Format for user message
)
def add_assistant_message(self, message: str):
"""Add an assistant message to the conversation history"""
self.conversation_history += (
f"<ASSISTANT> {message} </ASSISTANT>" # Format for assistant message
)
def get_response(self) -> str:
"""Get response from the model based on conversation history"""
# Convert the conversation history and model parameters into API arguments
api_kwargs = self.openai_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=self.conversation_history,
model_kwargs=self.model_kwargs,
model_type=ModelType.LLM,
)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}") # Debugging output to verify API parameters
# Call the API with the generated arguments to get a response
response = self.openai_client.call(
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, model_type=ModelType.LLM
)
print("response: ", response) # Debugging output for raw API response
# Extract and parse the text response from the API output
response_text = self.openai_client.parse_chat_completion(response)
# Update conversation history with the assistant's response
self.add_assistant_message(response_text)
return response_text # Return the assistant's response to the caller
Simulating a Multi-turn Conversation
In the check_chat_conversation() function, we simulate a multi-turn conversation by iterating over a list of user questions. Each question is added to the conversation history, and the assistant responds based on the accumulated conversation context.
def check_chat_conversation():
# Initialize a new chat conversation
chat = ChatConversation()
# Example list of user questions to simulate a multi-turn conversation
questions = [
"What is the capital of France?",
"What is its population?",
"Tell me about its famous landmarks",
]
# Iterate through each question in the list
for question in questions:
print(f"\nUser: {question}") # Display the user's question
chat.add_user_message(
question
) # Add the user question to the conversation history
response = (
chat.get_response()
) # Get assistant's response based on conversation history
print(f"Assistant: {response}") # Display the assistant's response
# Display the full conversation history after all exchanges
print("\nFull Conversation History:")
print(chat.conversation_history) # Print the accumulated conversation history
Key Points You can observe that each question is depended on previous question and the chat responds in apt manner check_chat_conversation()
OPENAI LLM Chat - Multichat Usage - Asynchronous¶
This example demonstrates how to create an asynchronous multichat system using OpenAI’s LLM with adalflow. The asynchronous approach allows handling multiple questions in parallel, making the interaction more efficient when dealing with unrelated queries.
import asyncio
from adalflow.components.model_client import OpenAIClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
from typing import List
ChatConversationAsync Class
The ChatConversationAsync class is designed to handle asynchronous API calls to the OpenAI model. It supports concurrent requests, which improves performance when interacting with multiple questions simultaneously.
class ChatConversationAsync:
def __init__(self):
# Initialize with an asynchronous OpenAI client
self.openai_client = OpenAIClient()
# Default model parameters for the chat
self.model_kwargs = {
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo", # Model used for chat
"temperature": 0.5, # Controls randomness in response
"max_tokens": 100, # Maximum tokens in the generated response
}
async def get_response(self, message: str) -> str:
"""Asynchronously get a response from the model for a given user message"""
# Convert input message and model parameters into the format expected by the API
api_kwargs = self.openai_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=message, # User's message input
model_kwargs=self.model_kwargs, # Model-specific settings
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Specify the model type as a language model (LLM)
)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}") # Log the API arguments for debugging
# Make an asynchronous API call to OpenAI's model
response = await self.openai_client.acall(
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, # Pass the prepared arguments
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Specify the model type again
)
print("response: ", response) # Print the raw response from the API
# Parse the API response to extract the assistant's reply (chat completion)
response_text = self.openai_client.parse_chat_completion(response)
return response_text # Return the parsed response text
Running Multiple Asynchronous Chat Sessions
In the check_chat_conversations_async() function, we handle a list of unrelated user questions concurrently. This is done by creating a list of asynchronous tasks and gathering their responses.
async def check_chat_conversations_async():
# Create an instance of ChatConversationAsync to handle asynchronous operations
chat = ChatConversationAsync()
# List of unrelated questions that will be handled in parallel
questions = [
"What is the capital of France?", # Question 1
"Is dog a wild animal?", # Question 2
"Tell me about amazon forest", # Question 3
]
# Create a list of asynchronous tasks, one for each question
# Each task calls the get_response method asynchronously for a question
tasks = [chat.get_response(question) for question in questions]
# Gather the results of all asynchronous tasks concurrently
responses = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
# Print the responses from the assistant along with the respective user questions
for question, response in zip(questions, responses):
print(f"\nUser: {question}")
print(f"Assistant: {response}")
Running the Asynchronous Function
To execute the asynchronous function, you can use the following methods based on your environment:
# Run the asynchronous function if in a file
# asyncio.run(check_chat_conversations_async())
# in jupyter notebook
await check_chat_conversations_async()
This approach allows you to handle multiple independent conversations concurrently, improving the system’s performance and responsiveness.
OPENAI LLM Chat - Multichat Usage - Benchmark sync() vs async()¶
This section compares the performance of synchronous (call()) vs. asynchronous (acall()) API calls to OpenAI’s language model, benchmarking them using a sample prompt to determine which approach is more efficient for handling multiple API requests.
import asyncio
import time
from adalflow.components.model_client import (
OpenAIClient,
) # Assuming OpenAIClient with .call() and .acall() is available
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
Setup for Benchmarking
We initialize the OpenAI client and set up a sample prompt to test both synchronous and asynchronous API calls.
# Initialize the OpenAI client
openai_client = OpenAIClient()
# Sample prompt for testing
prompt = "Tell me a joke."
model_kwargs = {"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo", "temperature": 0.5, "max_tokens": 100}
Synchronous Benchmarking
The benchmark_sync_call function runs the synchronous .call() method multiple times and measures the total time taken for all requests.
# Synchronous function for benchmarking .call()
def benchmark_sync_call(api_kwargs, runs=10):
"""
Benchmark the synchronous .call() method by running it multiple times.
Parameters:
- api_kwargs: The arguments to be passed to the API call
- runs: The number of times to run the call (default is 10)
"""
# List to store responses
responses = []
# Record the start time of the benchmark
start_time = time.time()
# Perform synchronous API calls for the specified number of runs
responses = [
openai_client.call(
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, # API arguments
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Model type (e.g., LLM for language models)
)
for _ in range(runs) # Repeat 'runs' times
]
# Record the end time after all calls are completed
end_time = time.time()
# Output the results of each synchronous call
for i, response in enumerate(responses):
print(f"sync call {i + 1} completed: {response}")
# Print the total time taken for all synchronous calls
print(f"\nSynchronous benchmark completed in {end_time - start_time:.2f} seconds")
# Asynchronous function for benchmarking .acall()
async def benchmark_async_acall(api_kwargs, runs=10):
"""
Benchmark the asynchronous .acall() method by running it multiple times concurrently.
Parameters:
- api_kwargs: The arguments to be passed to the API call
- runs: The number of times to run the asynchronous call (default is 10)
"""
# Record the start time of the benchmark
start_time = time.time()
# Create a list of asynchronous tasks for the specified number of runs
tasks = [
openai_client.acall(
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, # API arguments
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Model type (e.g., LLM for language models)
)
for _ in range(runs) # Repeat 'runs' times
]
# Execute all tasks concurrently and wait for them to finish
responses = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
# Record the end time after all tasks are completed
end_time = time.time()
# Output the results of each asynchronous call
for i, response in enumerate(responses):
print(f"Async call {i + 1} completed: {response}")
# Print the total time taken for all asynchronous calls
print(f"\nAsynchronous benchmark completed in {end_time - start_time:.2f} seconds")
api_kwargs = openai_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=prompt, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, model_type=ModelType.LLM
)
# Run both benchmarks
print("Starting synchronous benchmark...\n")
benchmark_sync_call(api_kwargs)
# Run the asynchronous function if in a file
# asyncio.run(benchmark_async_acall(api_kwargs))
print("\nStarting asynchronous benchmark...\n")
await benchmark_async_acall(api_kwargs)
OPENAI LLM Chat - Additional Utils¶
This section demonstrates the use of additional utility functions for OpenAI’s language model client. The following utility functions are included:
get_first_message_content()get_all_messages_content()get_probabilities()
These utilities can be used to interact with the OpenAI model in various ways, such as extracting the first message content, retrieving all message content from a multi-chat scenario, and calculating the probabilities of tokens.
Code Setup
First, we import necessary components for utilizing the OpenAI client and the utilities from the adalflow library.
from adalflow.components.model_client import OpenAIClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
from adalflow.utils import setup_env
from adalflow.components.model_client.openai_client import (
get_first_message_content,
get_all_messages_content,
get_probabilities,
)
from adalflow.core import Generator
Function: check_openai_additional_utils
This function demonstrates how to use the OpenAI client along with a custom utility function for generating responses from the model, based on the given query and utility function.
def check_openai_additional_utils(func, model_kwargs):
"""
This function demonstrates the usage of the OpenAI client and a custom utility function
for generating responses from the LLM model, based on the given query in openai client.
Parameters:
- func: A function that will be used to parse the chat completion (for custom parsing).
- model_kwargs: The additional model parameters (e.g., temperature, max_tokens) to be used in the model.
Returns:
- output: The generated response from the model based on the query.
"""
# Initialize the OpenAI client with a custom chat completion parser
openai_client = OpenAIClient(chat_completion_parser=func)
# Define a sample query (user question)
query = "What is the capital of France?"
# Set the model type to LLM (Large Language Model)
model_type = ModelType.LLM
# Create the prompt by formatting the user query as a conversation
prompt = f"User: {query}\n"
# Define any additional parameters needed for the model (e.g., the input string)
prompt_kwargs = {
"input_str": "What is the capital of France?",
}
# Initialize the Generator with the OpenAI client and model parameters
generator = Generator(model_client=openai_client, model_kwargs=model_kwargs)
# Execute the generator to get a response for the prompt (using the defined prompt_kwargs)
output = generator(prompt_kwargs=prompt_kwargs)
# Return the generated output (response from the LLM)
return output
Function: run_utils_functions
This function runs a series of utility functions using different model configurations for generating responses. It demonstrates how to check OpenAI model outputs using various utility functions.
def run_utils_functions():
"""
This function runs a series of utility functions using different model
configurations for generating responses. It demonstrates how to check
OpenAI model outputs using various utility functions.
"""
# Define the model arguments for the probability-based function (with logprobs)
probability_model_kwargs = {
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo", # Specify the model version
"logprobs": True, # Enable logprobs to get probability distributions for tokens
"n": 2, # Request 2 different completions for each query
}
# Define general model arguments for most other functions
model_kwargs = {
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo", # Specify the model version
"temperature": 0.5, # Control the randomness of responses (0 is deterministic)
"max_tokens": 100, # Set the maximum number of tokens (words) in the response
}
# List of functions to run with corresponding model arguments
func_list = [
[
get_probabilities,
probability_model_kwargs,
], # Function to get probabilities with specific kwargs
[
get_first_message_content,
model_kwargs,
], # Function to get first message content
[
get_all_messages_content,
model_kwargs,
], # Function to get all messages content in multi-chat scenarios
]
# Loop through each function and its corresponding arguments
for each_func in func_list:
# Check the function output using the specified arguments
result = check_openai_additional_utils(each_func[0], each_func[1])
# Print the function and result for debugging purposes
print(f"Function: {each_func[0].__name__}, Model Args: {each_func[1]}")
print(f"Result: {result}")
Running the Utility Functions
To execute the utility functions, we call the run_utils_functions() method, which runs the defined functions and prints their results.
run_utils_functions()
Purpose and Usage
These utilities (get_first_message_content, get_all_messages_content, and get_probabilities) allow users to extract specific information from the OpenAI LLM responses, such as individual message contents in a chat or the probability distribution over tokens.
Groq LLM Chat - Multichat Usage¶
Note: Groq doesnt have embedder method to get embeddings like openai
The following example demonstrates how to set up a multi-turn conversation with the Groq LLM using the GroqAPIClient.
from adalflow.components.model_client import GroqAPIClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
from adalflow.utils import setup_env
from typing import List, Dict
ChatConversation Class
This class handles the conversation flow by interacting with the Groq model, keeping track of the conversation history, and generating responses.
class ChatConversation:
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize a new ChatConversation object.
- GroqAPIClient is used to interact with the Groq model.
- conversation_history keeps track of the conversation between the user and assistant.
- model_kwargs contains the model parameters like temperature and max tokens.
"""
self.groq_client = (
GroqAPIClient()
) # Initialize GroqAPIClient for model interaction
self.conversation_history: str = (
"" # Initialize conversation history as an empty string
)
self.model_kwargs = {
"model": "llama3-8b-8192", # Specify the model to use
"temperature": 0.5, # Set the temperature for response variability
"max_tokens": 100, # Limit the number of tokens in the response
}
def add_user_message(self, message: str):
"""
Add a user message to the conversation history in the required format.
The message is wrapped with <USER> tags for better processing by the assistant.
"""
self.conversation_history += (
f"<USER> {message} </USER>" # Append user message to history
)
def add_assistant_message(self, message: str):
"""
Add an assistant message to the conversation history in the required format.
The message is wrapped with <ASSISTANT> tags for better processing.
"""
self.conversation_history += (
f"<ASSISTANT> {message} </ASSISTANT>" # Append assistant message to history
)
def get_response(self) -> str:
"""
Generate a response from the assistant based on the conversation history.
- Converts the conversation history and model kwargs into the format required by the Groq API.
- Calls the API to get the response.
- Parses and adds the assistant's reply to the conversation history.
"""
# Prepare the request for the Groq API, converting the inputs into the correct format
api_kwargs = self.groq_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=self.conversation_history, # Use the conversation history as input
model_kwargs=self.model_kwargs, # Include model-specific parameters
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Specify the model type (Large Language Model)
)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}") # Log the API request parameters
# Call the Groq model API to get the response
response = self.groq_client.call(
api_kwargs=api_kwargs,
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Specify the model type again for clarity
)
print("response: ", response) # Log the API response
# Parse the response to extract the assistant's reply
response_text = self.groq_client.parse_chat_completion(response)
# Add the assistant's message to the conversation history
self.add_assistant_message(response_text)
# Return the assistant's response text
return response_text
Example Multi-Turn Conversation
The following function simulates a multi-turn conversation, where the user asks a series of questions and the assistant responds. It demonstrates how user inputs are processed, and responses are generated while maintaining the conversation history.
def check_chat_conversation():
"""
This function simulates a multi-turn conversation between a user and an assistant.
It demonstrates how user inputs are processed, and the assistant generates responses,
while maintaining the conversation history for each query.
"""
# Initialize the ChatConversation object
chat = ChatConversation() # This creates an instance of the ChatConversation class
# Define a list of user questions for a multi-turn conversation
questions = [
"What is the capital of France?", # First user question
"What is its population?", # Second user question
"Tell me about its famous landmarks", # Third user question
]
# Loop through each question and get the assistant's response
for question in questions:
# Print the current question from the user
print(f"\nUser: {question}")
# Add the user's message to the conversation history
chat.add_user_message(question)
# Get the assistant's response based on the conversation history
response = chat.get_response()
# Print the assistant's response
print(f"Assistant: {response}")
# After the conversation, print the full conversation history
print("\nFull Conversation History:")
print(
chat.conversation_history
) # This will print all messages (user and assistant) in the conversation history
Run the following to use groq_client multichat ability
check_chat_conversation()
Groq LLM Chat - Multichat Usage - Asynchronous¶
This example demonstrates how to perform multi-turn conversations with the Groq LLM using asynchronous calls for each query. It uses Python’s asyncio to handle multiple independent requests concurrently.
import asyncio
from adalflow.components.model_client import GroqAPIClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
from typing import List
ChatConversation Class
This class allows you to interact asynchronously with the Groq model. The get_response method fetches responses from the model for a single user input asynchronously.
class ChatConversation:
def __init__(self):
# Using an asynchronous client for communication with GroqAPI
self.groq_client = GroqAPIClient() # Create an instance of GroqAPIClient
# Model configuration parameters (e.g., Llama model with 8b parameters and 8192 context length)
self.model_kwargs = {
"model": "llama3-8b-8192", # Llama model with specific size
"temperature": 0.5, # Degree of randomness in the model's responses
"max_tokens": 100, # Maximum number of tokens in the response
}
async def get_response(self, message: str) -> str:
"""Get response from the model for a single message asynchronously"""
# Convert the user input message to the appropriate format for the Groq API
api_kwargs = self.groq_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=message, # User's input message
model_kwargs=self.model_kwargs, # Model parameters
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Model type for large language models (LLM)
)
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}") # Print the API arguments for debugging
# Asynchronously call the Groq API with the provided API arguments
response = await self.groq_client.acall(
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, # Pass the API arguments
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Specify the model type
)
print("response: ", response) # Print the API response for debugging
# Parse the response to extract the assistant's reply from the API response
response_text = self.groq_client.parse_chat_completion(response)
return response_text # Return the assistant's response text
Example Asynchronous Multi-Turn Conversation
The following function demonstrates how multiple independent questions are handled asynchronously. Each question is processed concurrently, and their responses are gathered using asyncio.gather.
async def check_chat_conversations():
# Create an instance of ChatConversation
chat = ChatConversation()
# List of unrelated questions for independent async calls
questions = [
"What is the capital of France?",
"Is dog a wild animal ?",
"Tell me about amazon forest",
]
# Run each question as an independent asynchronous task
tasks = [chat.get_response(question) for question in questions]
# Gather all the responses concurrently
responses = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
# Display each response alongside the question
for question, response in zip(questions, responses):
print(f"\nUser: {question}")
print(f"Assistant: {response}")
To execute the function, run the following:
# Run the asynchronous function if in a file
# asyncio.run(check_chat_conversations())
await check_chat_conversations()
Groq LLM Chat - Multichat Usage - Benchmark sync() vs async()¶
This example demonstrates how to benchmark the synchronous .call() method versus the asynchronous .acall() method for making API calls using Groq. The benchmark compares the time taken to execute multiple API requests synchronously and asynchronously.
import asyncio
import time
from adalflow.components.model_client import (
GroqAPIClient,
) # Assuming GroqAPI with .call() and .acall() is available
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType
Initialization
The following code initializes the Groq client and sets up the sample prompt and model parameters for testing.
# Initialize the Groq client
groq_client = GroqAPIClient()
# Sample prompt for testing
prompt = "Tell me a joke."
model_kwargs = {"model": "llama3-8b-8192", "temperature": 0.5, "max_tokens": 100}
Benchmarking Synchronous .call() Method
This function benchmarks the synchronous .call() method by calling the Groq API synchronously multiple times.
# Synchronous function for benchmarking .call()
def benchmark_sync_call(api_kwargs, runs=10):
# List to store responses from each synchronous call
responses = []
# Record the start time for benchmarking
start_time = time.time()
# Perform synchronous API calls in a loop
responses = [
groq_client.call( # Calling the API synchronously
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, # Passing the API arguments
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Defining the model type
)
for _ in range(runs) # Repeat the call 'runs' times
]
# Record the end time after all calls are completed
end_time = time.time()
# Print out the response from each synchronous call
for i, response in enumerate(responses):
print(f"sync call {i + 1} completed: {response}")
# Print the total time taken for the synchronous benchmark
print(f"\nSynchronous benchmark completed in {end_time - start_time:.2f} seconds")
Benchmarking Asynchronous .acall() Method
This asynchronous function benchmarks the .acall() method by calling the Groq API asynchronously multiple times using asyncio.gather() to execute tasks concurrently.
# Asynchronous function for benchmarking .acall()
async def benchmark_async_acall(api_kwargs, runs=10):
# Record the start time for benchmarking
start_time = time.time()
# Create a list of tasks for asynchronous API calls
tasks = [
groq_client.acall( # Calling the API asynchronously
api_kwargs=api_kwargs, # Passing the API arguments
model_type=ModelType.LLM, # Defining the model type
)
for _ in range(runs) # Repeat the call 'runs' times
]
# Await the completion of all tasks concurrently
responses = await asyncio.gather(
*tasks
) # Gather all the responses from asynchronous calls
# Record the end time after all asynchronous calls are completed
end_time = time.time()
# Print out the response from each asynchronous call
for i, response in enumerate(responses):
print(f"Async call {i + 1} completed: {response}")
# Print the total time taken for the asynchronous benchmark
print(f"\nAsynchronous benchmark completed in {end_time - start_time:.2f} seconds")
Running the Benchmarks
The following code sets up the API arguments and runs both the synchronous and asynchronous benchmarks.
api_kwargs = groq_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=prompt, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, model_type=ModelType.LLM
)
# Run both benchmarks
print("Starting synchronous benchmark...\n")
benchmark_sync_call(api_kwargs)
print("\nStarting asynchronous benchmark...\n")
await benchmark_async_acall(api_kwargs)
Building Custom Model client¶
Building a Synchronous api call
Note: I am using openai api as a example to build custom model client in adalflow. Even though its already there in adalflow repo below code will definitly be a starter code whom ever wants to build a custom model client
# Building simple custom third party model client and using it
# I have modified convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs() to make sure it follows the prompt of openai and i have used appropiate
# openai api call in __call__()
import openai
from adalflow.core.model_client import ModelClient
from adalflow.core.types import ModelType, GeneratorOutput, EmbedderOutput
from openai.types import (
CreateEmbeddingResponse,
)
from adalflow.components.model_client.utils import parse_embedding_response
This class defines the custom model client. The constructor initializes the client by calling the parent class’s initializer (ModelClient), which is essential for the setup of the Adalflow framework.
class SimpleCustomModelClient(ModelClient):
# Initialize the custom model client
def __init__(self):
# Call the parent class's initializer
super().__init__()
pass # Placeholder for any initialization logic if needed in the future
# Method to convert input into API parameters for different model types (LLM or Embedder)
def convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
self, input=None, model_kwargs={}, model_type=ModelType.UNDEFINED
):
"""
Convert the inputs into API arguments based on the model type.
Args:
input (str): The input text to be processed.
model_kwargs (dict): Additional model parameters like temperature, max_tokens, etc.
model_type (ModelType): The type of model to use (LLM or Embedder).
Returns:
dict: API arguments formatted for the specified model type.
"""
if (
model_type == ModelType.LLM
): # If the model type is a large language model (LLM)
return {
"model": model_kwargs[
"model"
], # Set the model to use (e.g., GPT-3, GPT-4)
"messages": input, # Provide the input as the message
"temperature": model_kwargs[
"temperature"
], # Set the temperature (creativity of the response)
"max_tokens": model_kwargs[
"max_tokens"
], # Max tokens to generate in the response
}
elif model_type == ModelType.EMBEDDER: # If the model type is an embedder
return {
"model": model_kwargs["model"], # Model name for embedding
"input": [input], # Provide the input in a list format for embedding
}
else:
# Raise an error if the model type is unsupported
raise ValueError(f"model_type {model_type} is not supported")
# Method to make the actual API call to OpenAI for either completions (LLM) or embeddings
def call(self, api_kwargs={}, model_type=ModelType.UNDEFINED):
"""
Call the appropriate OpenAI API method based on the model type (LLM or Embedder).
Args:
api_kwargs (dict): Arguments to be passed to the API call.
model_type (ModelType): The type of model (LLM or Embedder).
Returns:
Response: The API response from OpenAI.
"""
if model_type == ModelType.LLM: # If the model type is LLM (e.g., GPT-3, GPT-4)
return openai.chat.completions.create(
**api_kwargs
) # Call the chat API for completion
elif model_type == ModelType.EMBEDDER: # If the model type is Embedder
return openai.embeddings.create(**api_kwargs) # Call the embedding API
else:
# Raise an error if an invalid model type is passed
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported model type: {model_type}")
# Method to parse the response from a chat completion API call
def parse_chat_completion(self, completion):
"""
Parse the response from a chat completion API call into a custom output format.
Args:
completion: The completion response from the OpenAI API.
Returns:
GeneratorOutput: A custom data structure containing the parsed response.
"""
# Note: GeneratorOutput is a adalflow dataclass that contains the parsed completion data
return GeneratorOutput(
data=completion, # Store the raw completion data
error=None, # No error in this case
raw_response=str(completion), # Store the raw response as a string
)
# Method to parse the response from an embedding API call
def parse_embedding_response(
self, response: CreateEmbeddingResponse
) -> EmbedderOutput:
"""
Parse the response from an embedding API call into a custom output format.
Args:
response (CreateEmbeddingResponse): The response from the embedding API.
Returns:
EmbedderOutput: A custom data structure containing the parsed embedding response.
"""
try:
# Attempt to parse the embedding response using a helper function
return parse_embedding_response(response)
except Exception as e:
# If parsing fails, return an error message with the raw response
return EmbedderOutput(data=[], error=str(e), raw_response=response)
In below block, the custom model client is instantiated, and a query is defined for processing by both an LLM (like GPT-3.5) and an Embedder model. The API arguments are converted, and the call() method is used to fetch responses. Finally, both types of responses (LLM and Embedder) are parsed and printed.
def build_custom_model_client():
# Instantiate the custom model client (SimpleCustomModelClient)
custom_client = SimpleCustomModelClient()
# Define the query for the model to process
query = "What is the capital of France?"
# Set the model type for a Large Language Model (LLM)
model_type = ModelType.LLM
# Prepare the message prompt as expected by the OpenAI chat API.
# This format is suitable for GPT-like models (e.g., gpt-3.5-turbo).
message_prompt = [
{
"role": "user", # Define the user role in the conversation
"content": [
{
"type": "text", # Specify that the input is a text type
"text": query, # The actual query to be processed by the model
}
],
}
]
# Print message indicating the usage of the LLM model type
print("ModelType LLM")
# Define additional model parameters like model name, temperature, and max tokens for LLM
model_kwargs = {"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo", "temperature": 0.5, "max_tokens": 100}
# Convert the input message and model kwargs into the required API parameters
api_kwargs = custom_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=message_prompt, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, model_type=model_type
)
# Print the API arguments that will be passed to the call method
print(f"api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}")
# Call the LLM model using the prepared API arguments
result = custom_client.call(api_kwargs, ModelType.LLM)
# Print the result of the LLM model call (response from OpenAI)
print(result)
# Parse the chat completion response and output a more structured result
response_text = custom_client.parse_chat_completion(result)
# Print the structured response from the chat completion
print(f"response_text: {response_text}")
# Switch to using the Embedder model type
print("ModelType EMBEDDER")
# Define model-specific parameters for the embedding model
model_kwargs = {
"model": "text-embedding-3-small",
"dimensions": 8,
"encoding_format": "float",
}
# Convert the input query for the embedder model
api_kwargs = custom_client.convert_inputs_to_api_kwargs(
input=query, model_kwargs=model_kwargs, model_type=ModelType.EMBEDDER
)
# Print the API arguments that will be passed to the embedder model
print(f"embedder api_kwargs: {api_kwargs}")
# Call the Embedder model using the prepared API arguments
result = custom_client.call(api_kwargs, ModelType.EMBEDDER)
# Print the result of the Embedder model call (embedding response)
print(result)
# Parse the embedding response and output a more structured result
response_text = custom_client.parse_embedding_response(result)
# Print the structured response from the embedding model
print(f"response_text: {response_text}")
This is the function call that triggers the execution of the custom model client, processing the defined query and displaying results for both LLM and Embedder.
build_custom_model_client()
